Introduction
Dealing with skin conditions such as eczema, psoriasis, and dermatitis can be challenging and often takes a toll on one’s self-esteem and overall well-being. The redness, itchiness, and discomfort associated with these conditions can significantly impact daily life. However, there are various solutions available to help transform troubled skin and provide relief. In this article, we will explore effective strategies and treatments to manage eczema, psoriasis, and dermatitis, allowing individuals to regain control over their skin health and improve their quality of life.
Table of Contents
- Understanding Eczema, Psoriasis, and Dermatitis
- What is Eczema?
- What is Psoriasis?
- What is Dermatitis?
- Identifying Triggers and Prevention
- Common Triggers
- Prevention Strategies
- Topical Treatments for Troubled Skin
- Moisturizers and Emollients
- Steroid Creams and Ointments
- Topical Calcineurin Inhibitors
- Antihistamines
- Coal Tar Preparations
- Phototherapy and Light Therapy
- UVB Phototherapy
- PUVA Therapy
- Excimer Laser Therapy
- Systemic Medications
- Oral Corticosteroids
- Immunosuppressants
- Biologic Therapies
- Natural Remedies and Alternative Therapies
- Aloe Vera
- Coconut Oil
- Dead Sea Salt Baths
- Herbal Supplements
- Lifestyle Changes for Skin Health
- Diet and Nutrition
- Stress Management
- Skincare Routine
- Seeking Professional Help and Support
- Dermatologists
- Support Groups
- Conclusion
1. Understanding Eczema, Psoriasis, and Dermatitis
What is Eczema?
Eczema, also known as atopic dermatitis, is a chronic skin condition characterized by inflamed, itchy, and dry patches of skin. It commonly affects children but can persist into adulthood. The exact cause of eczema is unknown, but it is believed to involve a combination of genetic and environmental factors.
What is Psoriasis?
Psoriasis is an autoimmune disease that results in the rapid buildup of skin cells, leading to thick, red, and scaly patches. It commonly affects the elbows, knees, scalp, and lower back. Psoriasis is a chronic condition that can come and go in cycles, with triggers such as stress, infections, and certain medications.
What is Dermatitis?
Dermatitis refers to inflammation of the skin, which can have various causes, including allergies, irritants, or genetic factors. It presents as a rash, redness, swelling, and itchiness. Contact dermatitis occurs when the skin comes into contact with a substance that triggers an allergic reaction or irritation.
2. Identifying Triggers and Prevention
Common Triggers
Identifying triggers is crucial for managing troubled skin conditions. Some common triggers for eczema, psoriasis, and dermatitis include:
- Allergens such as pollen, dust mites, pet dander, and certain foods
- Irritants like soaps, detergents, perfumes, and certain fabrics
- Stress and emotional factors
- Weather changes, particularly cold and dry climates
- Infections and injuries to the skin
Prevention Strategies
To prevent flare-ups and minimize symptoms, consider the following strategies:
- Avoid known triggers and allergens
- Use gentle, fragrance-free soaps and detergents
- Keep the skin well-moisturized
- Wear soft, breathable fabrics
- Manage stress through relaxation techniques and self-care
3. Topical Treatments for Troubled Skin
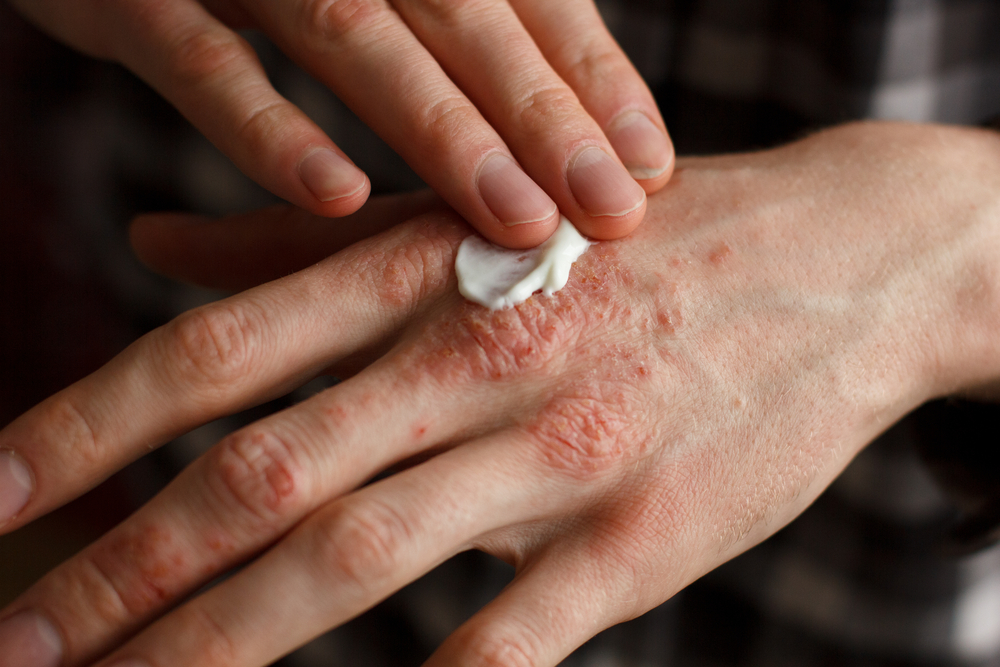
Topical treatments are often the first line of defense in managing eczema, psoriasis, and dermatitis. They aim to reduce inflammation, relieve itching, and hydrate the skin. Some commonly used topical treatments include:
Moisturizers and Emollients
Regularly applying moisturizers and emollients helps lock in moisture and create a protective barrier on the skin. Look for products containing ingredients like ceramides, hyaluronic acid, and shea butter for optimal hydration.
Steroid Creams and Ointments
Corticosteroid creams and ointments are effective in reducing inflammation and itching. They come in different strengths, and your dermatologist will prescribe the appropriate one based on the severity of your condition.
Topical Calcineurin Inhibitors
Calcineurin inhibitors, such as tacrolimus and pimecrolimus, are non-steroidal creams that help modulate the immune response in the skin, reducing inflammation and controlling symptoms.
Antihistamines
Antihistamines can help relieve itching associated with troubled skin conditions. They work by blocking the effects of histamine, a substance released during an allergic reaction.
Coal Tar Preparations
Coal tar preparations have been used for decades to treat psoriasis and dermatitis. They help slow down excessive skin cell growth and reduce inflammation.
4. Phototherapy and Light Therapy
Phototherapy and light therapy involve exposing the skin to specific wavelengths of light to reduce inflammation and promote healing. Some common types of phototherapy include:
UVB Phototherapy
UVB phototherapy uses ultraviolet B light to penetrate the skin and slow down the rapid growth of skin cells. It can be done under the supervision of a dermatologist or using a home UVB unit.
PUVA Therapy
PUVA therapy combines a photosensitizing medication called psoralen with UVA light exposure. This treatment is effective for psoriasis and involves carefully timed exposure to UVA light after taking the medication.
Excimer Laser Therapy
Excimer laser therapy delivers targeted UVB light to affected areas, reducing inflammation and promoting healthy skin growth. It is commonly used for localized psoriasis plaques.
5. Systemic Medications
In severe cases of troubled skin conditions, when topical treatments and light therapy are not sufficient, systemic medications may be prescribed. These medications work from within the body to target the underlying causes. Some examples include:
Oral Corticosteroids
Oral corticosteroids are prescribed for short-term use to quickly reduce inflammation and symptoms. However, long-term use can lead to side effects, so they are generally used for acute flare-ups.
Immunosuppressants
Immunosuppressant medications suppress the immune system to prevent it from attacking the skin. They are often used in severe cases of psoriasis or dermatitis.
Biologic Therapies
Biologic therapies are a newer class of medications that target specific molecules involved in the immune response. They have shown remarkable effectiveness in managing moderate to severe psoriasis and dermatitis.
6. Natural Remedies and Alternative Therapies
While natural remedies and alternative therapies may not replace medical treatments, some individuals find them beneficial as adjunct therapies. It is important to consult with a healthcare professional before using any natural remedies. Some options to consider include:
Aloe Vera
Aloe vera has soothing properties and can help alleviate itching and inflammation. Apply pure aloe vera gel to the affected areas for relief.
Coconut Oil
Coconut oil is known for its moisturizing properties and can help soothe dry, itchy skin. Apply organic, cold-pressed coconut oil to the troubled areas regularly.
Dead Sea Salt Baths
Taking baths with Dead Sea salt can provide relief for troubled skin. The minerals in the salt help reduce inflammation and promote healing.
Herbal Supplements
Certain herbal supplements, such as fish oil, evening primrose oil, and Oregon grape, have shown potential in managing eczema, psoriasis, and dermatitis. However, more research is needed to establish their effectiveness.
7. Lifestyle Changes for Skin Health
In addition to medical treatments, making certain lifestyle changes can contribute to overall skin health and reduce the frequency and severity of flare-ups. Consider the following:
Diet and Nutrition
A well-balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can support skin health. Avoiding trigger foods, such as dairy, gluten, and processed foods, may also be beneficial for some individuals.
Stress Management
Stress can exacerbate troubled skin conditions. Explore stress management techniques like meditation, yoga, and deep breathing exercises to help reduce stress levels.
Skincare Routine
Adopt a gentle skincare routine using mild cleansers and moisturizers. Avoid harsh exfoliants or scrubbing the skin vigorously, as this can worsen symptoms.
8. Seeking Professional Help and Support
If you are struggling with eczema, psoriasis, or dermatitis, it is essential to seek professional help. Dermatologists specialize in diagnosing and treating skin conditions and can provide personalized recommendations based on your specific needs. Additionally, consider joining support groups where you can connect with others who understand your journey and share experiences and coping strategies.
Conclusion
Transforming troubled skin affected by eczema, psoriasis, or dermatitis is possible through a combination of medical treatments, lifestyle changes, and self-care. Understanding the nature of your condition, identifying triggers, and seeking professional help are crucial steps toward finding relief and improving your quality of life. By implementing the strategies and treatments outlined in this article, you can take control of your skin health and experience the transformation you deserve.

Leave a comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *