Erythema, a common skin condition characterized by redness and inflammation, can affect people of all ages and skin types. This article delves into the various causes of erythema and explores effective treatment options to alleviate its symptoms and promote healthier skin.
Introduction
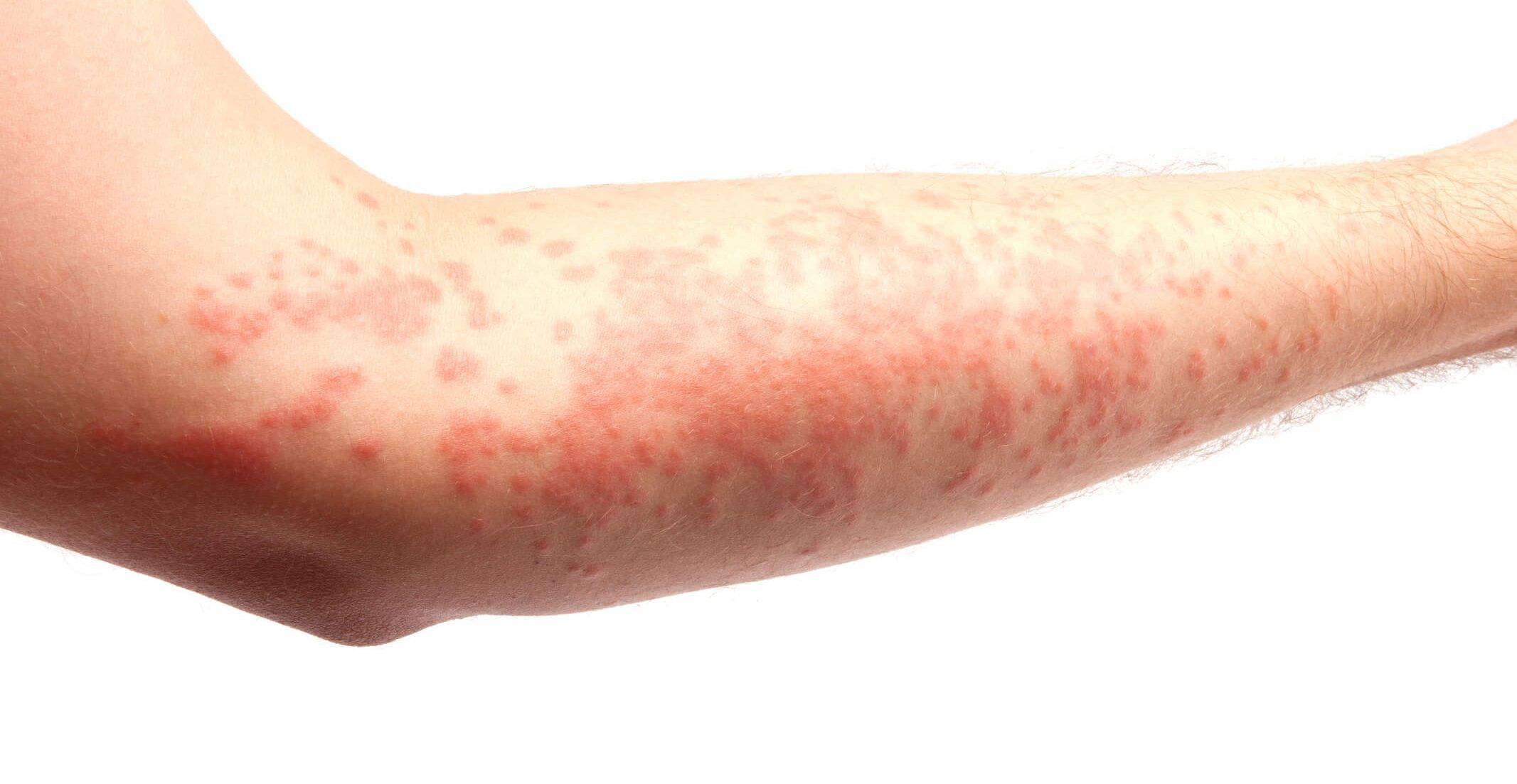
Erythema, often referred to as redness or skin flushing, is a skin condition that can arise for various reasons. It manifests as red, inflamed patches on the skin’s surface, and understanding its causes and treatment options is crucial for managing the condition effectively.
Understanding Erythema
What is Erythema?
Erythema is a skin condition characterized by the reddening of the skin due to increased blood flow to the affected area. It can occur in response to various stimuli, ranging from external triggers to internal factors.
Types of Erythema
There are several types of erythema, each with distinct underlying causes. These include erythema multiforme, erythema nodosum, and erythema migrans. The type of erythema a person experiences depends on the specific factors triggering the condition.
Common Symptoms
Symptoms of erythema can vary based on the type and severity of the condition. Common signs include redness, warmth, swelling, and sometimes pain or itchiness in the affected area. The appearance of the skin may also change, becoming more sensitive and reactive.
Causes of Erythema
Sun Exposure and UV Radiation
Excessive sun exposure and ultraviolet (UV) radiation are leading triggers of erythema. UV rays can damage the skin’s DNA, leading to inflammation and redness. It’s important to use sunscreen and protective clothing to minimize the risk of sun-induced erythema.
Skin Allergies
Allergic reactions to certain substances, such as cosmetics, detergents, or plants, can result in erythema. The body’s immune response to allergens can lead to skin inflammation and redness.
Inflammatory Skin Conditions
Conditions like eczema, psoriasis, and rosacea can cause chronic inflammation, leading to erythema. Managing these underlying conditions is essential in preventing recurring episodes of skin redness.
Infections
Bacterial, viral, or fungal infections can trigger erythema as the body’s immune system responds to the presence of pathogens. Erythema may be a symptom of an underlying infection that needs prompt medical attention.
Medications
Some medications, particularly certain antibiotics and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), can cause erythema as a side effect. It’s important to discuss potential side effects with a healthcare provider when prescribed new medications.
Diagnosing Erythema
Physical Examination
A dermatologist can diagnose erythema through a physical examination of the affected area. The appearance, distribution, and characteristics of the redness help determine the possible cause.
Medical History
Providing a comprehensive medical history, including recent exposures, allergies, and medications, assists in narrowing down the potential causes of erythema.
Biopsy and Laboratory Tests
In some cases, a skin biopsy or laboratory tests may be necessary to confirm the underlying cause of erythema. These tests can provide valuable insights into the nature of the condition.
Treatment Options
Topical Creams and Ointments
Topical corticosteroids and anti-inflammatory creams can help reduce redness and inflammation associated with erythema. These medications are often prescribed based on the severity of the condition.
Oral Medications
For more severe cases, oral medications like antihistamines or immunosuppressants may be recommended to control the immune response and alleviate symptoms.
Laser and Light Therapies
Laser treatments and phototherapy can target specific blood vessels and reduce redness in certain types of erythema. These therapies are performed under the guidance of a dermatologist.
Moisturization and Skin Care
Maintaining proper skincare and moisturization can help manage erythema and prevent flare-ups. Fragrance-free and gentle skincare products are often recommended.
Preventing Erythema
Sun Protection Measures
Using sunscreen with a high SPF, wearing protective clothing, and avoiding prolonged sun exposure can significantly reduce the risk of sun-induced erythema.
Allergen Avoidance
Identifying and avoiding allergens that trigger skin reactions is essential for preventing erythema related to allergies.
Healthy Lifestyle Choices
Adopting a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet, regular exercise, and stress management, can contribute to overall skin health and minimize erythema triggers.
Lifestyle Tips for Managing Erythema
Choosing Suitable Skincare Products
Opt for gentle and hypoallergenic skincare products to avoid exacerbating erythema. Always perform a patch test before using new products.
Dietary Considerations
Certain foods, such as spicy foods and alcohol, can trigger erythema in some individuals. Pay attention to your body’s reactions and make dietary adjustments if necessary.
Stress Management
Stress can exacerbate skin conditions like erythema. Engage in relaxation techniques, such as meditation and deep breathing, to manage stress levels.
Consulting a Dermatologist
When to Seek Professional Help
If erythema persists, worsens, or is accompanied by other concerning symptoms, it’s advisable to consult a dermatologist for proper evaluation and treatment.
What to Expect During the Visit
During the dermatologist visit, the healthcare provider will assess the condition, discuss potential triggers, and recommend a personalized treatment plan.
Conclusion
Erythema, characterized by redness and inflammation of the skin, can be triggered by various factors, including sun exposure, allergies, and skin conditions. While it can be concerning, effective management is possible through proper skincare, lifestyle adjustments, and medical interventions. By understanding the causes and following preventive measures, individuals can achieve healthier and more comfortable skin.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- Is erythema a serious medical condition?
- Erythema can vary in severity, and while it is not always serious, persistent or severe cases should be evaluated by a dermatologist.
- Can I use over-the-counter creams for erythema?
- Mild cases of erythema may improve with over-the-counter creams, but it’s best to consult a healthcare professional for personalized recommendations.
- Are there any natural remedies for erythema?
- Some natural ingredients like aloe vera and chamomile may offer relief, but their effectiveness varies. Consult a dermatologist for guidance.
- Can stress really trigger erythema?
- Yes, stress can contribute to erythema flare-ups in some individuals, as it can exacerbate underlying skin conditions.
- Is erythema contagious?
- No, erythema itself is not contagious. It is a response of the skin to various triggers and is not caused by bacteria or viruses.

Leave a comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *